PhD student
Email

Carlos Ibanez Lab @ PKU & CIBR
McGovern Institute at Peking University & Chinese Institute for Brain Research
PhD student
Email


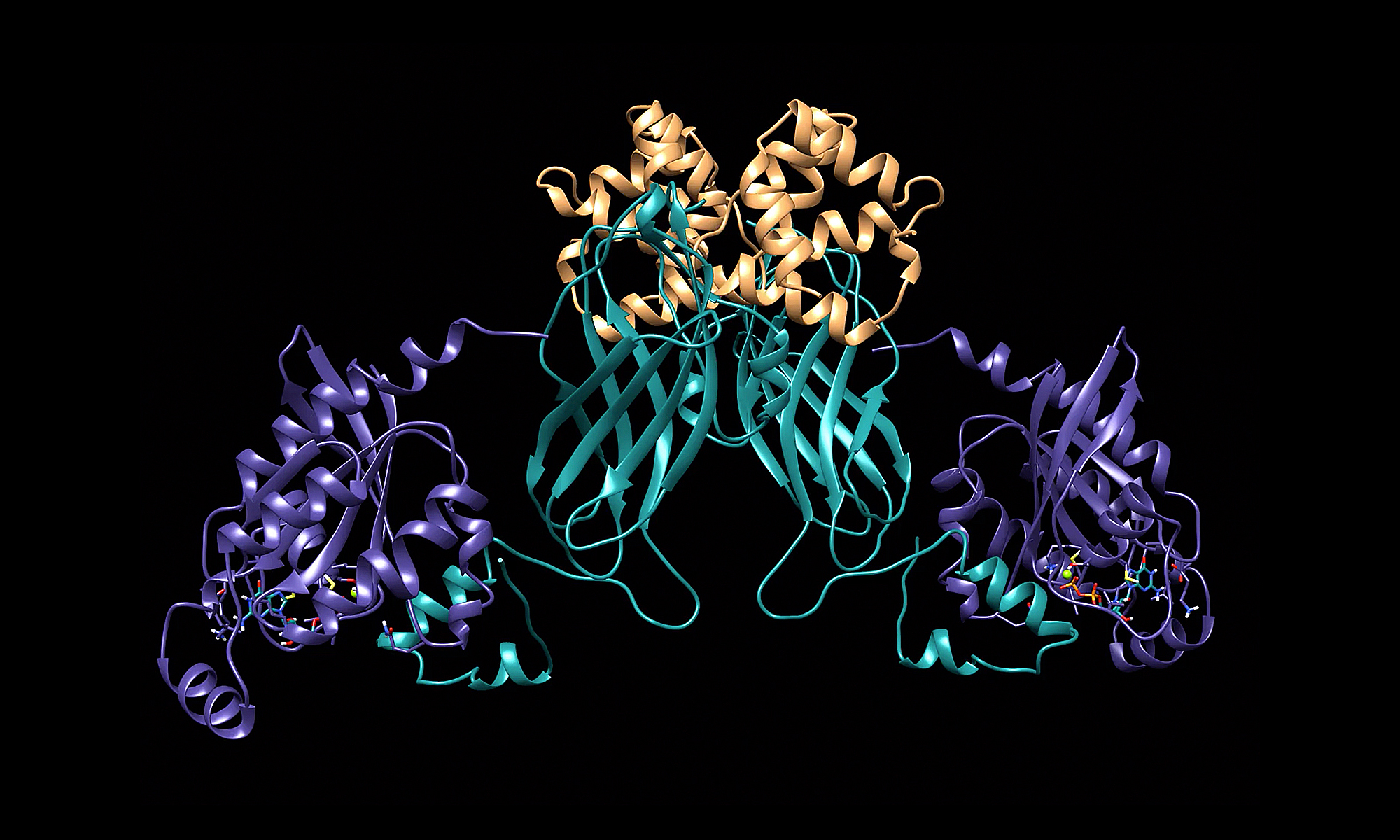
RhoGDI phosphorylation by PKC promotes its interaction with death receptor p75 NTR to gate axon growth and neuron survival
Ajeena Ramanujan , Zhen Li, Yanchen Ma, Zhi Lin & Carlos F. Ibáñez (2024)
EMBO Reports doi.org/10.1038/s44319-024-00064-2
Click on thumbnail to display PDF
How receptors juggle their interactions with multiple downstream effectors remains poorly understood.
In our latest paper, we report that the outcome of death receptor p75NTR signaling is determined through competition of effectors for interaction with its intracellular domain, in turn dictated by the nature of the ligand. While NGF induces release of RhoGDI through recruitment of RIP2, thus decreasing RhoA activity in favor of NFkB signaling, MAG induces PKC-mediated phosphorylation of the RhoGDI N-terminus, promoting its interaction with the juxtamembrane domain of p75NTR, disengaging RIP2, and enhancing RhoA activity in detriment of NF-kB. This results in stunted neurite outgrowth and apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons. If presented simultaneously, MAG prevails over NGF. The NMR solution structure of the complex between the RhoGDI N-terminus and p75NTR juxtamembrane domain reveals previously unknown structures of these proteins and clarifies the mechanism of p75NTR activation.
These results show how ligand-directed competition between RIP2 and RhoGDI for p75NTR engagement determine axon growth and neuron survival. Similar principles are likely at work in other receptors engaging multiple effectors and signaling pathways.
The paper has been published in EMBO Reports
Read the full paper HERE
Adipocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy are the two main processes contributing to adipose tissue expansion, yet the mechanisms that regulate and balance their involvement in obesity are incompletely understood. Activin B/GDF-3 receptor ALK7 is expressed in mature adipocytes and promotes adipocyte hypertrophy upon nutrient overload by suppressing adrenergic signaling and lipolysis. In contrast, the role of ALK4, the canonical pan-activin receptor, in adipose tissue is unknown.
In our latest paper, we report that, unlike ALK7, ALK4 is preferentially expressed in adipocyte precursors, where it suppresses differentiation, allowing proliferation and adipose tissue expansion. ALK4 expression in adipose tissue increases upon nutrient overload and positively correlates with fat depot mass and body weight, suggesting a role in adipose tissue hyperplasia during obesity. Mechanistically, ALK4 signaling suppresses expression of CEBPα and PPARγ, two master regulators of adipocyte differentiation. Conversely, ALK4 deletion enhances CEBPα/PPARγ expression and induces premature adipocyte differentiation, which can be rescued by CEBPα knockdown.
These results clarify the function of ALK4 in adipose tissue and highlight the contrasting roles of the two activin receptors in the regulation of adipocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy during obesity.
The paper has been published in The Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Read the full paper HERE

Activin receptor ALK4 promotes adipose tissue hyperplasia by suppressing differentiation of adipocyte precursors
Ee-Soo Lee , Tingqing Guo, Raj Kamal Srivastava, Assim Shabbir & Carlos F. Ibáñez
The Journal of Biological Chemistry (2022) doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102716
Click on thumbnail to display PDF
Administrative Assistant
Email

ΔfosB is an alternatively spliced product of the FosB gene that is essential for dopamine-induced reward pathways and that acts as a master switch for addiction. However, the molecular mechanisms of its generation and regulation by dopamine signaling are unknown.
In this new paper, we report that dopamine D1 receptor signaling synergizes with the activin/ALK4/Smad3 pathway to potentiate the generation of ΔFosB mRNA in medium spiny neurons (MSNs) of the nucleus accumbens (NAc) via activation of the RNA-binding protein PCBP1, a regulator of mRNA splicing. Concurrent activation of PCBP1 and Smad3 by D1 and ALK4 signaling induced their interaction, nuclear translocation, and binding to sequences in exon-4 and intron-4 of FosB mRNA. Ablation of either ALK4 or PCBP1 in MSNs impaired ΔFosB mRNA induction and nuclear translocation of ΔFosB protein in response to repeated co-stimulation of D1 and ALK4 receptors. Finally, ALK4 is required in NAc MSNs of adult mice for behavioral sensitization to cocaine.
These findings uncover an unexpected mechanism for ΔFosB generation and drug-induced sensitization through convergent dopamine and ALK4 signaling.
The paper has been published in The EMBO Journal
Read the full paper HERE

Convergent dopamine and ALK4 signaling to PCBP1 controls FosB alternative splicing and cocaine behavioral sensitization
Favio A Krapacher , Diana Fernandez-Suarez, Annika Andersson , Alvaro Carrier-Ruiz & Carlos F. Ibáñez (2021)
The EMBO Journal (2022) e110721
Click on thumbnail to display PDF